Molecule. Imagine a future where maintaining a healthy weight and optimizing your metabolism doesn’t solely rely on grueling workouts or restrictive diets.
What if a simple molecule could unlock the same profound benefits as intense physical activity and fasting, but without the physical exertion or hunger pangs?
This might sound like science fiction, or perhaps another fleeting “miracle cure” in the ever-evolving landscape of health trends. However, groundbreaking research from Denmark suggests that such a future could be closer than we think.
Molecule, Beyond Diets and Dogma.
A Novel Approach to Wellness.
For years, the pursuit of leanness and optimal health has often been synonymous with strict dietary regimens and demanding exercise routines.
While the undisputed benefits of physical activity and mindful eating are well-documented, from reducing the risk of serious diseases and combating depression to improving cognitive function.
The reality is that these paths aren’t accessible or sustainable for everyone.
Life circumstances, medical conditions, or simply a lack of time can make consistent adherence to such lifestyles a significant challenge.
This is where the innovative work of Danish doctors comes into play. Researchers at Aarhus University have developed a pioneering molecule that could mimic the physiological effects of both fasting and strenuous exercise within the body.
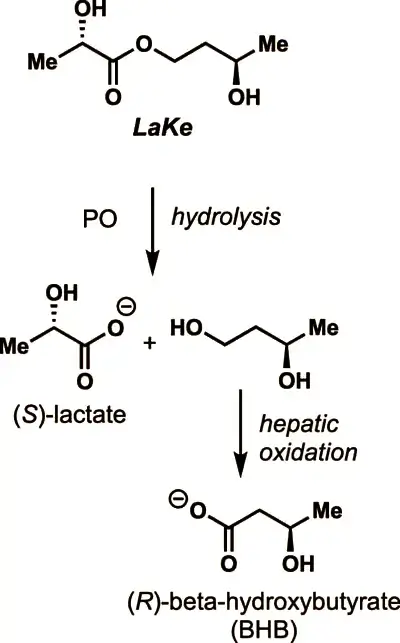
Named “LaKe”… a charmingly apt moniker that hints at its function – this molecule holds the potential to revolutionize how we approach metabolic health and weight management.
The Science Behind “LaKe”.
Mimicking Nature’s Benefits.
Our bodies are incredibly sophisticated machines, and the benefits of activities like fasting and intense exercise stem from specific biochemical changes.
When we fast or engage in vigorous physical activity, our bodies naturally increase the production of certain compounds, notably lactate (a salt of lactic acid) and ketones.
These substances don’t just signal a state of exertion; they become vital “fuel” for our cells, triggering a cascade of beneficial metabolic responses.
The Aarhus University experts, whose findings were published in the prestigious Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, delved deep into these mechanisms. They observed that elevated levels of lactate and ketones in the bloodstream lead to several key physiological changes:
• Increased production of appetite-suppressing hormones: This is a crucial aspect for weight management, as it helps to naturally regulate hunger and satiety.
• Decreased levels of free fatty acids in the blood: This contributes to overall metabolic health and reduces the risk of conditions like metabolic syndrome.
The researchers emphasize that achieving such a potent and comprehensive metabolic shift through diet alone is incredibly difficult, if not impossible.
While lactate and ketones are naturally produced, consuming them in sufficient quantities from external sources without undesirable acidic and salty byproducts has proven to be a significant hurdle.
This is precisely where the LaKe molecule offers a groundbreaking solution. When introduced into the body, LaKe effectively increases the levels of lactate and ketones without producing these unwanted byproducts. In essence, it provides the “good” without the “bad.”
Promising Results and Future Prospects.
Initial experiments with mice have yielded highly encouraging results, demonstrating that the LaKe molecule can artificially regulate lactate and ketone levels safely and effectively. This opens up exciting possibilities for its application as a potential new dietary supplement.
The next critical step involves the first clinical trials in humans, which have already commenced at Aarhus University.
If these trials prove successful, a LaKe-based supplement could become a game-changer for individuals who, for various reasons, are unable to engage in regular or intense physical activity. This includes people with medical conditions, busy professionals, or those with mobility issues.
Moreover, the potential benefits of the LaKe molecule extend beyond weight management and general metabolic health.
Researchers believe it could also play a role in improving cognitive function, particularly in conditions characterized by low brain energy levels, such as Parkinson’s disease and dementia. By supplying the brain with efficient fuel, LaKe might help to restore proper neurological function.
The Unseen Impact of Sedentary Lifestyles.
A Deeper Dive into Heart Health.
The importance of this research is further underscored by a fascinating study on the human heart and its adaptation to physical activity (or lack thereof). Our hearts are not just pumps; they are dynamic organs that adapt to our lifestyles.
Dr. Robert Shave from the University of British Columbia and his colleagues conducted a comparative study of heart shape and performance across gorillas, chimpanzees, and four distinct groups of humans: long-distance runners, American football players, “subsistence” farmers, and sedentary city dwellers.
The findings revealed compelling insights into the evolution and adaptation of the human heart. Gorillas and chimpanzees, despite their incredible bursts of strength and activity, generally lead less active lives and spend a significant amount of time resting.
Their hearts are adapted to these patterns: thick muscular walls and a more rounded shape.
The human heart, on the other hand, is more elongated, primarily due to an enlarged left ventricle responsible for pumping oxygenated blood throughout the body. Crucially, the human heart exhibits a slight twisting motion with each beat.
This unique twisting allows for greater blood expulsion with each contraction and more efficient filling when it relaxes between beats. Ape hearts, according to Shave and his co-authors, lack this twisting capability, resulting in more limited blood-pumping efficiency. However, their hearts are better adapted to sudden bursts of activity and operate under higher blood pressure.
The “Ape Heart” Phenomenon.
A Call to Action.
The study revealed a stark and concerning trend: the hearts of individuals unaccustomed to physical activity gradually lose many of their “human characteristics.”
They become more rounded and exhibit less pronounced twisting during work, surprisingly, even less than chimpanzees. Furthermore, similar consequences were observed in football players who, despite years of training for explosive power, developed thicker heart muscle walls but displayed weaker adaptations related to endurance.
This “ape heart” phenomenon highlights the profound impact of a sedentary lifestyle on our cardiovascular health. It underscores that consistent, endurance-based activity is crucial for maintaining the unique efficiency and adaptability of the human heart.
And this is where the connection to the LaKe molecule becomes strikingly clear. For those unable to engage in the necessary physical activity to preserve their heart’s optimal function, or for those seeking to mitigate the negative metabolic impacts of a less active lifestyle, a molecule like LaKe could offer a vital lifeline.
It presents a potential pathway to achieve some of the core benefits of exercise and fasting, protecting not just our waistlines but also the very engine of our bodies.
In a world where health challenges are increasingly prevalent, the development of the LaKe molecule offers a beacon of hope, promising a future where wellness is more attainable for everyone.
What are your thoughts on this potential breakthrough? Do you think a molecule like LaKe could truly change how we approach health and fitness?
Have a Great Day!