Diseases. Many prevalent diseases advance almost unnoticed, their symptoms often dismissed or attributed to everyday stresses. However, these insidious conditions can lead to severe complications and even premature death if left unaddressed.
This article will delve into these “silent killers,” providing essential insights into their nature, early detection, and preventive measures.
Diseases, What Are “Silent Killers” and Why Are They So Dangerous?
The term “silent killer” refers to diseases that show few or no obvious symptoms in their early stages, making them particularly dangerous.
Experts often use this term to highlight their ability to conceal symptoms for extended periods, silently damaging the body. The deceptive nature of these diseases means their early signs are frequently masked by general fatigue or work-related stress.
Consequently, the only reliable way to detect these pathologies early is through regular medical check-ups and preventive screenings. Early diagnosis is crucial, as timely intervention can significantly improve treatment outcomes and, without a doubt, save lives.
Common Factors Contributing to Silent Killers.
Various changes in bodily function typically arise from an unhealthy lifestyle, including inadequate nutrition, physical inactivity, and obesity.
Many of these diseases develop over years, yet a majority of people tend to overlook the initial warning signs and subtle symptoms. Recognizing these underlying causes is the first step toward prevention.
High Blood Pressure (Hypertension).
The World Health Organization identifies high blood pressure as the primary alarming indicator for vascular diseases, such as stroke, which can be a direct cause of death.
Normal blood pressure is generally considered to be around 120/80 mmHg, with minor upward fluctuations being normal after exercise or stress.
The Problem: Hypertension often arises from obesity, prolonged use of hormonal medications, or excessive consumption of salty or fatty foods.
The insidious nature of high blood pressure lies in its gradual development, allowing the body to adapt to the changes and pressure spikes. Individuals may stop experiencing significant discomfort, only occasionally noticing dizziness or a sensation of heat.
What You Can Do: The single most effective measure for early diagnosis is the regular use of a tonometer (blood pressure monitor).
Monitoring your readings 3-4 times a week can help identify elevated blood pressure before it leads to serious complications. Lifestyle modifications, such as adopting a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management, are also vital for prevention and control.
Liver Disease (Hepatic Steatosis or Fatty Liver).
Fatty liver, or hepatic steatosis, is a common condition that is often challenging to diagnose without an ultrasound. But what exactly does “fatty liver” mean?
The Problem: In this condition, liver cells actively accumulate fat molecules, failing to break them down and remove them from the body. Causes include hormonal imbalances, thyroid pathology, or adrenal tumors.
Several risk factors increase the likelihood of developing fatty liver:
• Metabolic disorders
• Diabetes mellitus
• Atherosclerosis
• Polycystic ovaries in women
In its initial stages, hepatic steatosis develops without symptoms. Over time, a dull, dragging pain may appear on the right side of the abdomen, typically when 10% of the liver tissue has been replaced by fat deposits.
If left untreated, the liver’s function can be severely impaired, leading to digestive issues and systemic intoxication.
What You Can Do?
While early symptoms are rare, lifestyle changes are paramount for prevention and management. These include maintaining a healthy weight, limiting processed foods and sugary drinks, and avoiding excessive alcohol consumption.
Regular medical check-ups, including blood tests and potential imaging, can help in early detection, especially if you have risk factors.
Ischemic Heart Disease (IHD).
Ischemic heart disease occurs when cholesterol deposits accumulate on the walls of the coronary arteries, reducing blood flow to the heart muscle.
This can lead to cell death and a slowdown of blood circulation throughout the body, causing oxygen deprivation in the brain and other internal organs, potentially resulting in a myocardial infarction (heart attack).
What You Can Do?
To prevent ischemic heart disease, it’s crucial to adopt a heart-healthy lifestyle. This includes:
• Quitting smoking and reducing alcohol consumption: Both habits significantly increase the risk of heart disease.
• Managing weight: Excess weight puts added strain on the heart.
• Stress management: Chronic stress can contribute to cardiovascular problems.
• Regular exercise and a balanced diet: These are fundamental for maintaining a healthy heart and blood vessels.
Diabetes Mellitus.
Often referred to by doctors as a “silent killer,” diabetes can develop without obvious symptoms for a long time. Intense thirst, unexplained weight loss, or vision problems often appear only when vascular damage is already significant, such as at the stage of kidney dysfunction.
The Problem: In diabetes, metabolism slows down, and the body either stops producing the hormone insulin (Type 1) or becomes resistant to its effects (Type 2). This leads to elevated blood glucose levels, which can damage various organs and systems over time.
What You Can Do?
A simple blood glucose test can help detect negative changes in time and prevent complications. Regular screenings are especially important if you have risk factors like a family history of diabetes, obesity, or a sedentary lifestyle.
Managing blood sugar through diet, exercise, and medication (if prescribed) is essential for preventing long-term complications.
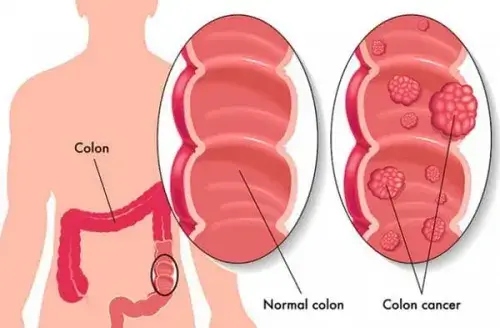
Bowel Cancer (Colorectal Cancer).
Worldwide, the incidence of colorectal cancer is rapidly increasing. Unfortunately, many patients are diagnosed at a late stage (stages 3-4), which significantly diminishes their chances of a long and active life.
The Problem: Bowel cancer often develops from a benign polyp in the large intestine over several years. However, this growth can only be detected through a colonoscopy. Because of its slow progression and lack of early symptoms, colon cancer is a prime example of a silent killer.
What You Can Do?
Doctors recommend that all patients over the age of 45-50 undergo a preventive colonoscopy, even in the absence of painful symptoms.
Early detection of polyps allows for their removal before they become cancerous, dramatically improving prognosis. Regular screening is the most effective prevention strategy.
Osteoporosis.
Osteoporosis is a disease that leads to the thinning of bone tissue, resulting in frequent and severe fractures that heal poorly.
It often develops due to a deficiency of calcium and vitamin D in the diet, and in women, it is frequently linked to hormonal imbalances.
What You Can Do?
Start prevention after 40-45 years of age. Incorporate the following into your lifestyle:
• Regular exercise: Weight-bearing exercises and swimming can strengthen bones.
• Calcium-rich diet: Consume dairy products, leafy greens, and fortified foods.
• Vitamin D: Ensure adequate vitamin D intake through sunlight exposure or supplements.
• Avoid alcohol and nicotine: Both can negatively impact bone health.
Cervical Cancer.
The primary reason for advanced cervical cancer is often a woman’s reluctance to treat dysplasia in its early stages. This disease can transform into cancer due to injuries and inflammation of the cervix, which are preventable in 90% of cases.
Risk Factors: Patients who are obese or infected with certain types of the human papillomavirus (HPV) are at higher risk.
What You Can Do?
The best prevention method is an annual gynecological examination including a Pap test, and timely treatment of erosion and infections. The HPV vaccine is also a highly effective preventive measure against the types of HPV that cause most cervical cancers.
Skin Cancer.
Among oncological and pathological conditions, skin cancer ranks second in terms of mortality. It often develops over many years, largely due to excessive sun exposure and an overindulgence in tanning beds.
What You Can Do?
If you notice non-healing ulcers, peeling, or redness on your skin, consult a dermatologist immediately.
Do not attempt self-treatment, as early diagnosis is crucial for successful treatment. Regular self-examinations of your skin and professional skin checks are also recommended, especially if you have a history of significant sun exposure or a large number of moles.
Viral Hepatitis (Hepatitis B and C).
When liver cells are damaged by Hepatitis B or C viruses, inflammation begins, leading to irreversible changes in the organ’s structure.
These diseases can progress asymptomatically for several years, destroying liver lobes and provoking the formation of fibrosis and cirrhosis.
The Problem: The asymptomatic nature of these diseases and the absence of characteristic signs often lead to a delayed visit to the doctor, by which point significant liver damage may have occurred.
What You Can Do?
A blood test can help identify the pathology in its early stages, and it is recommended to undergo this test at least once a year, especially if you are at risk.
In many cases, these diseases can be completely cured if detected and treated in their early stages. Vaccination against Hepatitis B is also a highly effective preventive measure.
The Importance of Prevention and Early Detection.
It is crucial to remember the paramount importance of prevention and regular check-ups. Annual screenings and being attuned to subtle changes in your body can prevent serious complications and improve your quality of life.
Don’t wait for symptoms to become severe; be proactive about your health.
Stay healthy and well! Have a good day!