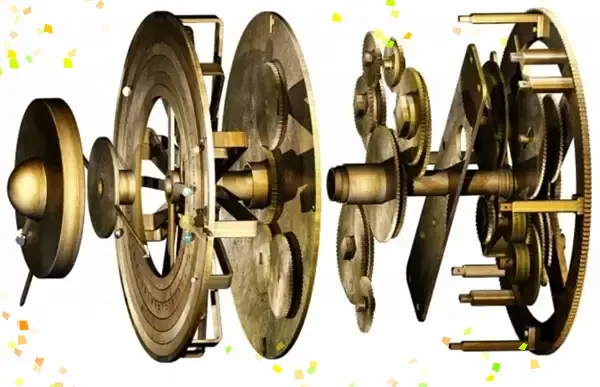
Computer in History, Introduction to the Antikythera Mechanism. The Antikythera Mechanism, often hailed as the first analog computer- WOW!
Is a remarkable artifact that emerged from ancient Greece around the second century BCE.
Discovered in 1901 in a shipwreck off the coast of the Greek island of Antikythera, this intricate device consists of a complex arrangement of gears and dials that showcases the advanced engineering capabilities of the time.
 The mechanism’s primary purpose was to predict astronomical positions and eclipses for calendrical and astrological purposes, a reflection of the era’s deep fascination with celestial bodies and their movements.
The mechanism’s primary purpose was to predict astronomical positions and eclipses for calendrical and astrological purposes, a reflection of the era’s deep fascination with celestial bodies and their movements.
Computer in History, Antikythera Mechanism.
During the Hellenistic period, when the Antikythera Mechanism was created, significant advancements were taking place in various fields such as mathematics, astronomy, and engineering.
Scholars like Aristarchus of Samos and Hipparchus were pioneering early theories about the solar system, proposing heliocentric models and systematic observations of stars and planets.
The cultural environment of this time was characterized by a synthesis of knowledge from different civilizations, including Babylonian, Egyptian, and Indian influences.
This confluence of ideas led to remarkable achievements in understanding the cosmos, which the Antikythera Mechanism embodies.
The historical significance of the Antikythera Mechanism extends beyond its technological sophistication.
It also serves as a vital artifact that reveals insights into the scientific and philosophical mindset of ancient Greek society.
The intricate design and functionality suggest a level of mathematical precision and mechanical expertise that was unprecedented for its time and was not replicated until the onset of the Middle Ages.
By examining this ancient device, modern scholars can glean important information about the levels of knowledge and technological progress achieved by the Greeks in astronomy and mechanics, thereby enriching our understanding of their contributions to the scientific heritage of humanity.
The Functionality of the Antikythera Mechanism.
The Antikythera Mechanism is an ancient Greek invention that functioned as a sophisticated analog computer, demonstrating a deep understanding of astronomy and mechanics during its time.
Typically housed in a wooden frame, the device comprised an intricate assembly of gears, carefully designed to track the movements of celestial bodies.
By observing these movements, the mechanism could predict astronomical events, including eclipses and planetary transitions, functioning almost like a calendar.
The intricate gears provided precise calculations that represented the cycles of the moon, sun, and planets.
One of the most remarkable features of the Antikythera Mechanism is its ability to predict eclipses.
The device utilized the Saros cycle, a period of approximately 18 years during which eclipses recur at regular intervals.
This capability indicates that its creators not only had an exceptional grasp of mechanical engineering but also possessed advanced knowledge of the cyclical nature of celestial phenomena.
The gears and mechanisms worked in tandem, allowing users to input specific dates, which the device would then leverage to display the corresponding celestial events.
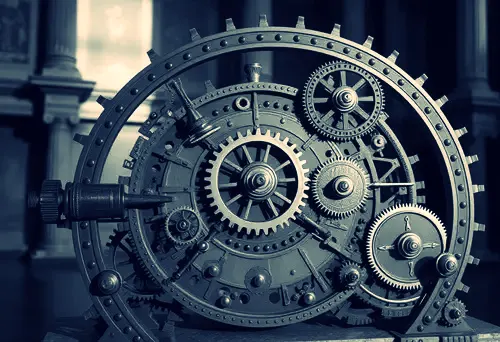 The engineering marvel of the Antikythera Mechanism is further illustrated through its design of differential gears, which facilitated the calculation of planetary positions.
The engineering marvel of the Antikythera Mechanism is further illustrated through its design of differential gears, which facilitated the calculation of planetary positions.
Each gear was meticulously crafted, often made of bronze and engraved with astronomical inscriptions.
These gears interacted with one another in a layered arrangement, allowing for precise movement to represent the complex motions of celestial bodies across various timeframes.
This ancient device not only paved the way for future astronomical instruments but also showcased the ingenuity of its creators in merging art and science.
Historical Impact and Legacy.
The Antikythera Mechanism, often regarded as the earliest known analogue computer, has had a profound impact on the fields of science and technology since its discovery.
Unearthed in 1901 from a shipwreck off the coast of Antikythera, Greece, this ancient artifact has prompted extensive research into its purpose and sophistication.
Prior to the mechanism’s discovery, there was little understanding of the technical achievements of ancient civilizations, particularly in the realms of astronomy and mechanical engineering.
The intricate gears and the predictive capabilities of the Antikythera Mechanism challenged the long-held assumption that such complex devices were solely a feature of the Renaissance or later periods.
As researchers have delved deeper into its design and functionality, the Antikythera Mechanism has revealed insights into the technological prowess of the ancient Greeks.
It not only functioned as a calendar but also predicted astronomical events such as eclipses, showcasing an advanced understanding of celestial mechanics.
This remarkable device has been instrumental in reshaping our perception of ancient technology, highlighting that the roots of computational devices can be traced back thousands of years, long before the advent of modern computing.
The legacy of the Antikythera Mechanism extends beyond its historical significance.
It has inspired contemporary scientists and engineers to explore the origins of technology, spurring a renewed interest in the capabilities of ancient civilizations.
Furthermore, its design principles have influenced modern astronomical instruments and computational devices, demonstrating the timeless nature of innovative thought.
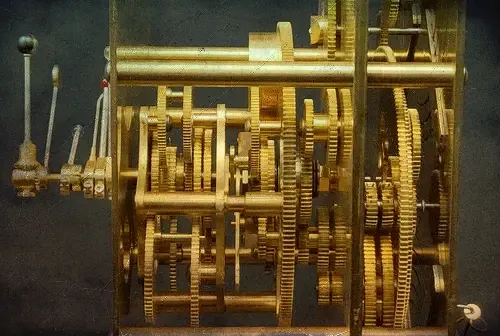 Through exhibitions and scholarly research, the Antikythera Mechanism continues to captivate audiences, serving as a symbol of human ingenuity that transcends time and remains relevant in discussions surrounding the evolution of technology and science.
Through exhibitions and scholarly research, the Antikythera Mechanism continues to captivate audiences, serving as a symbol of human ingenuity that transcends time and remains relevant in discussions surrounding the evolution of technology and science.
Modern Discoveries and Ongoing Research.
The Antikythera Mechanism, often referred to as the world’s first computer, has been the subject of extensive research since its discovery in the early 20th century.
Recent advancements in imaging technologies, particularly X-ray computed tomography (CT) and three-dimensional (3D) modeling, have significantly enhanced our understanding of this ancient artifact.
These modern methods allow researchers to visualize the intricate internal structure of the Mechanism without causing any damage to the fragile components.
With the help of these technologies, scientists have uncovered previously unseen inscriptions, shed light on the operation of the gears, and reconstructed the device’s complex calendar system.
Moreover, ongoing studies have revealed crucial insights into the astronomical calculations that the Antikythera Mechanism was capable of performing.
 The device appears to have been designed not only for predicting celestial events but also for displaying a comprehensive understanding of the cosmological model of the ancient Greeks.
The device appears to have been designed not only for predicting celestial events but also for displaying a comprehensive understanding of the cosmological model of the ancient Greeks.
The implications of these findings are profound, as they suggest a much higher level of sophistication in ancient scientific knowledge than previously acknowledged.
Despite these advances, researchers continue to face challenges in fully deciphering the workings and purposes of the Mechanism.
Some aspects, such as the function of certain gears or the complete understanding of its astronomical models, remain elusive.
This ongoing research raises important questions regarding the technological capabilities of ancient civilizations.
The insights gained from the study of the Antikythera Mechanism not only enrich our knowledge of classical antiquity but also stimulate further investigation into other ancient technologies, thereby broadening our understanding of historical scientific development.
As researchers piece together the puzzle of this remarkable device, it continues to captivate both scholars and enthusiasts alike, reaffirming its status as a transformative relic of human ingenuity.
You Good Day!